Kenya nairobi flooding – Kenya’s capital, Nairobi, faces a daunting challenge as relentless flooding wreaks havoc on its infrastructure, homes, and communities. Understanding the causes, consequences, and mitigation strategies of these floods is crucial for addressing this pressing issue.
The city’s flood-prone areas, heavily influenced by topography, drainage systems, and infrastructure, bear the brunt of these inundations. Torrential rainfall, inadequate drainage, and urbanization exacerbate the situation, while deforestation further diminishes water retention capacity.
Nairobi’s Flood-Prone Areas
Nairobi is prone to flooding due to various factors, including heavy rainfall, poor drainage systems, urbanization, and deforestation. The most flood-prone areas in Nairobi include:
- Korogocho
- Kibera
- Mathare
- Huruma
- Kariobangi
These areas are located in low-lying areas, have poor drainage systems, and are densely populated, making them particularly vulnerable to flooding.
Causes of Flooding in Nairobi
Flooding in Nairobi is caused by a combination of factors, including:
- Heavy rainfall and poor drainage systems:Nairobi experiences heavy rainfall during the rainy season, which can overwhelm the city’s drainage systems, leading to flooding.
- Urbanization and increased impervious surfaces:As Nairobi continues to grow, more land is being covered by impervious surfaces, such as roads and buildings, which reduces the amount of water that can be absorbed into the ground and increases runoff.
- Deforestation and reduced water retention capacity:Deforestation in the Nairobi area has reduced the city’s water retention capacity, making it more susceptible to flooding.
- Climate change:Climate change is leading to more frequent and intense rainfall events, which is expected to increase the frequency and severity of flooding in Nairobi.
Consequences of Flooding in Nairobi: Kenya Nairobi Flooding
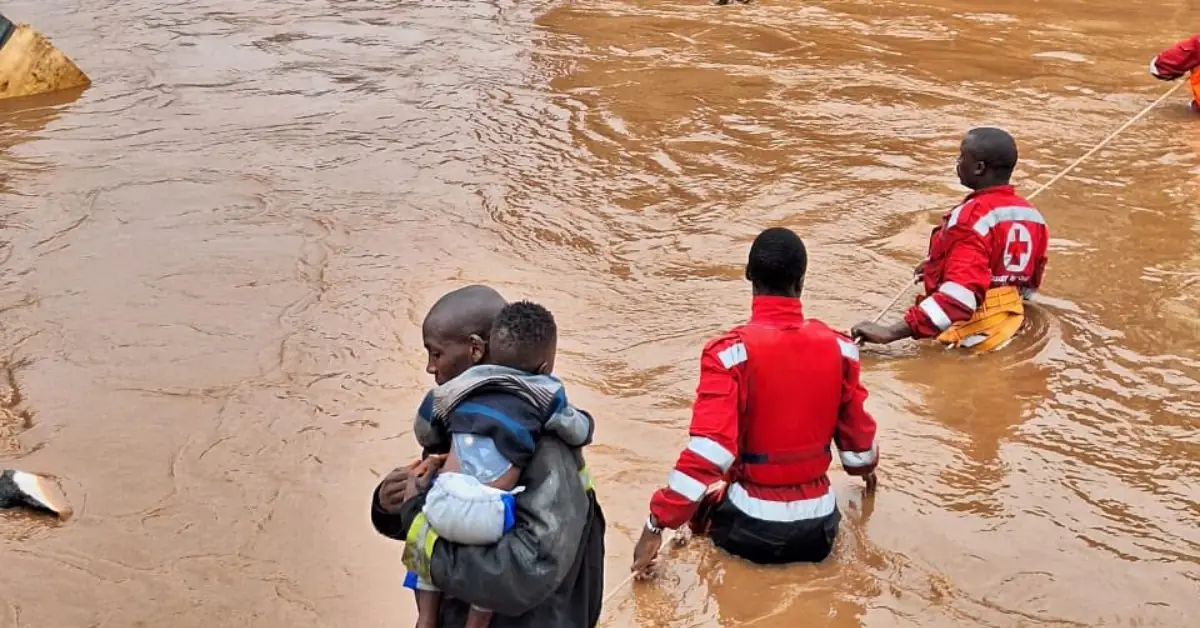

Flooding in Nairobi has a number of immediate and long-term consequences, including:
- Damage to infrastructure, homes, and businesses:Flooding can damage roads, bridges, buildings, and other infrastructure, as well as homes and businesses.
- Loss of life and displacement of residents:Flooding can lead to loss of life and displacement of residents, particularly in informal settlements.
- Disruption of transportation and essential services:Flooding can disrupt transportation and essential services, such as water and electricity.
- Health hazards and spread of waterborne diseases:Flooding can create health hazards, such as the spread of waterborne diseases.
Flood Mitigation and Management Strategies
There are a number of strategies that can be implemented to mitigate and manage flooding in Nairobi, including:
- Improving drainage systems and infrastructure:Improving the city’s drainage systems and infrastructure can help to reduce flooding.
- Implementing flood warning systems and evacuation plans:Implementing flood warning systems and evacuation plans can help to save lives and reduce the impact of flooding.
- Promoting sustainable land use practices:Promoting sustainable land use practices, such as reducing impervious surfaces and increasing green space, can help to reduce flooding.
- Raising awareness and educating the public about flood risks:Raising awareness and educating the public about flood risks can help to reduce the impact of flooding.
Final Summary
Nairobi’s battle against flooding requires a multi-faceted approach. Improving drainage systems, implementing early warning systems, and promoting sustainable land use practices are essential. Additionally, embracing technology, such as remote sensing and GIS mapping, can enhance flood monitoring and risk assessment.
Collaboration with other cities and international organizations is invaluable in sharing best practices and securing funding. By addressing the root causes and implementing effective mitigation strategies, Nairobi can work towards a more resilient and flood-resistant future.
FAQ Section
What are the most flood-prone areas in Nairobi?
Low-lying areas near rivers and streams, such as Kibera, Mathare, and Huruma, are particularly susceptible to flooding.
How does urbanization contribute to flooding?
Increased impervious surfaces, such as roads and buildings, reduce water absorption, leading to higher runoff and flooding.
What are the health hazards associated with flooding?
Flooding can spread waterborne diseases such as cholera, typhoid, and dysentery, posing a significant health risk to affected communities.